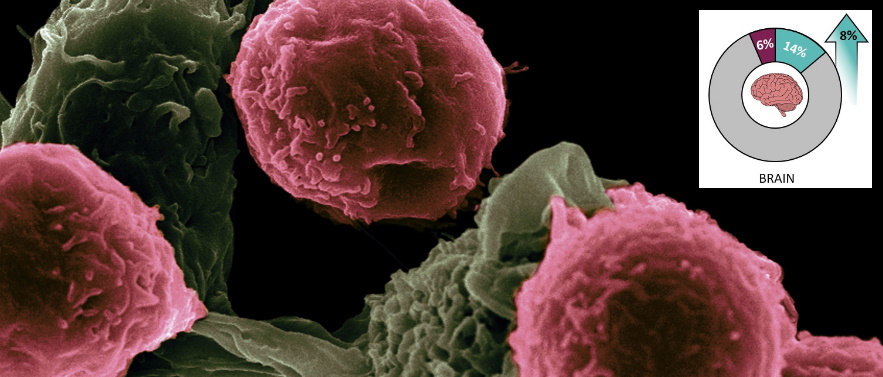
Glioblastoma (GBM) is a malignant form of brain tumour. Around eight new cases of primary brain tumours are diagnosed for every 100,000 people each year – in other words about 4,500 new cases in the UK annually. About 70% to 80% of primary brain tumours are High Grade Gliomas.
The current clinical standard of treatment for GBM is surgical resection followed by chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy. In most cases, complete tumour resection is not feasible making local recurrence inevitable. In addition, many patients are not eligible for surgery due to co-morbidities or proximity of the tumour to vital structures. Chemotherapy drugs have poor penetration through the BBB leading to ineffective concentrations reaching the tumour site.